Aluminium Flanges
Trusted manufacturer of precision aluminium flanges for seamless piping connections. We provide custom sizes, pressure ratings, and finishes to meet your project needs. Fast delivery, competitive pricing, and global shipping available.
Aluminum Flange is a pipe connection component made of aluminum alloy, providing a detachable interface capable of withstanding high pressure and high temperature. They are used as connectors between pipes, valves, pumps, and other equipment, facilitating assembly and disassembly while ensuring leak-proof joints.
Aluminum flanges are made from various aluminum alloys (such as 5086, 6061, 6063, etc.), characterized by corrosion resistance, lightweight, relatively low cost, and stable performance, making them suitable for marine, industrial, and HVAC applications.
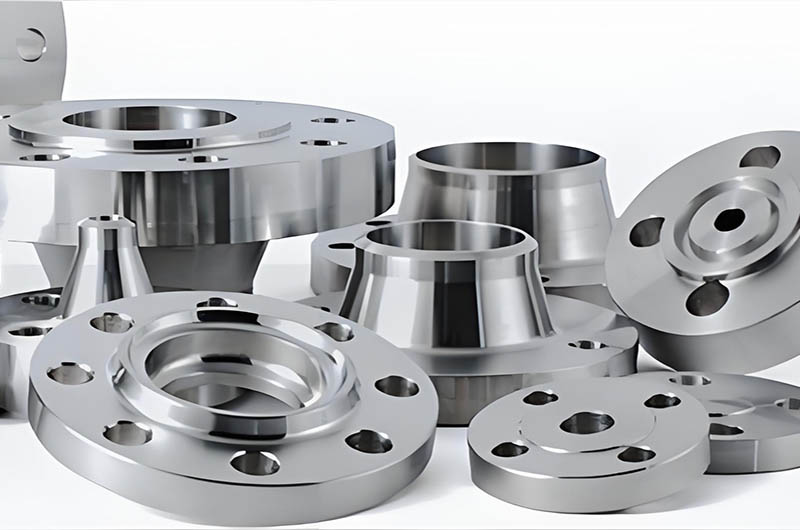

The Role of Aluminum Flanges in Piping Systems
Aluminum flanges are aluminum flange fittings commonly used at the ends of pipes to connect with valves, pumps, instruments, or other equipment. Their core function is to connect pipes, valves, or equipment, ensuring fluid-tight transmission while allowing for easy disassembly and maintenance.
Main Components of Aluminum Flanges
- Main Structure: Usually circular or ring-shaped, with a central hole matching the pipe diameter.
- Sealing Surface: Common types include Flat Face (FF), Raised Face (RF), and Male-Female (MFM), designed to work with gaskets to prevent leakage.
- Bolt Holes: Evenly distributed along the flange edge, used to secure the flange with bolts to its counterpart.
- Flange Neck (Exclusive to Weld Neck Flanges): An extended section welded to the pipe to enhance structural strength.
Specification of Haomei Aluminium Flanges Products Detial
| Aluminium Flanges | Flange Type | SO,BL, PL,WN,TH,SW,LJ |
| Material | 1000-7000 Series | |
| Size Range | 1/2''-24'' | |
| Class | 150LBS-2500LBS, PN6-PN40 | |
| Surface Treatment | Anodized | |
| Standard | ANSI B16.5,ANSI B16.47,DIN2576,DIN2502, DIN2527,JIS |
Note: These abbreviations refer to the most commonly used types of pipe flanges in piping systems. In short:
- SO – Slip-On Flange: This flange slips over the pipe and is then fillet welded on both the inner and outer surfaces.
- BL – Blind Flange: A solid disc with bolt holes, used to close or seal off the end of a piping system.
- PL – Plate Flange (sometimes called "flat welding flange"): A flat or standard flange type welded to the pipe; similar to a slip-on flange but without a prominent neck.
- WN – Weld Neck Flange: Features a long tapered hub that is butt-welded to the pipe, providing high strength and stress distribution.
- TH – Threaded Flange: Has an internal thread that mates with a corresponding threaded pipe, eliminating the need for welding.
- SW – Socket Weld Flange: The pipe is inserted into a recessed "socket" and then welded around the joint; commonly used in small-diameter, high-pressure applications.
- LJ – Lap Joint Flange: Used with a stub end (support flange) and is easy to disassemble; the flange itself is not welded to the pipe.
Haomei Aluminum strictly controls material composition, forging temperature, and heat treatment parameters to prevent defects such as porosity and cracks. We have integrated production capabilities including forging, heat treatment, machining, surface treatment, and packaging & shipment.
Types of Aluminum Flanges
Classification of Aluminum Flange Sealing Surfaces
- Flat Face Flange (FF): The flange face is flat, commonly used in low-pressure and moderate-temperature environments.
- Raised Face Flange (RF): The flange face is slightly raised, suitable for higher pressure and temperature fluctuations.
- Male-Female Flange (MF): The flange face is recessed, primarily used in applications requiring higher sealing performance.
- Back-to-Back Flange (BB): Two flanges are installed face-to-face with a sealing gasket in between, suitable for high-pressure and high-temperature environments.
Classification of Aluminum Flange Connection Methods
| Flange Type | Flange Image | Description |
| Aluminum Slip-On Flanges |

|
Welded to the outer surface of the pipe, suitable for low-pressure systems. Its design allows it to easily slide over the pipe end and be secured in place through welding. This type of flange has a simple structure, is easy to install, and has a lower cost, making it ideal for low-pressure piping systems. |
| Aluminum Weld Neck Flanges |

|
Butt-welded to the pipe through its neck, capable of withstanding high-pressure and high-temperature environments. Its tapered hub design helps distribute stress evenly within the piping system, enhancing structural strength and reducing stress concentration in the welded area. Due to its superior performance, weld neck flanges are commonly used in high-demand industrial applications such as oil, gas, and aerospace. |
| Aluminum Threaded Flanges |

|
Connected to pipes through internal threads, eliminating the need for welding, making installation and disassembly easier. These flanges are suitable for low-pressure and non-high-temperature environments and are commonly found in piping systems requiring frequent maintenance, such as water supply lines, fire protection systems, and HVAC systems. Their threaded connection minimizes the need for welding equipment, making them an ideal choice for quick installations. |
| Aluminum Blind Flanges |

|
Used to close the end of a pipe, helping to isolate fluids or gases in the system. Its solid, hole-free design provides a high-strength seal, effectively preventing leaks while allowing for pressure testing and maintenance operations. Blind flanges are ideal for inspection, expansion, or termination points in piping systems and are widely used in chemical, energy, and marine industries. |
| Aluminum Socket Weld Flanges |

|
The pipe is inserted into the recessed socket of the flange and welded around the joint to ensure a secure connection. This design is suitable for small-diameter, high-pressure piping systems, such as precision hydraulic pipelines and gas distribution lines. Socket weld flanges provide excellent strength and sealing capabilities while minimizing turbulence inside the welded joint. |
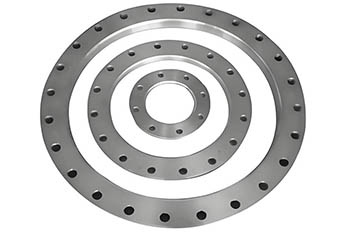
| Aluminum Plate Flanges |
|
A simple flat welding flange that is usually welded to the pipe and used in low to medium-pressure systems. Its design is similar to a slip-on flange but without a prominent neck, making it easier to manufacture and install. Plate flanges are widely used in light industries, building pipelines, and shipbuilding due to their cost-effectiveness and ease of processing. |
Characteristics and Materials of Aluminum Flanges
Aluminum Alloy Flange Characteristics
- Lightweight and Corrosion Resistance: Aluminum is much lighter than steel, reducing the overall system weight and making installation easier. Its naturally formed protective oxide layer provides excellent corrosion resistance, a key advantage in harsh or humid environments.
- Strength-to-Weight Ratio and Thermal Conductivity: Despite its low density, aluminum has a high strength-to-weight ratio. It also exhibits excellent thermal conductivity, allowing it to quickly absorb and dissipate heat—an important property for applications where temperature management is crucial.
- Mechanical Properties: Depending on the alloy and temper condition used, aluminum flanges are designed to withstand a range of pressures—from low-pressure systems (such as PN10) to high-pressure applications—while maintaining sufficient ductility and tensile strength.
- Easy Machining: Aluminum flanges can be cast, forged, or machined at a relatively low cost.
Aluminum Alloy Flange Grades and Materials
Material Types: Common aluminum alloy grades include 6061-T6 (high strength), 5086, 5083 (corrosion resistance), 7075 (aerospace applications), and 2024.
- 5083: Known for its corrosion resistance, suitable for marine environments or chemical industries.
- 6061-T6: After heat treatment, it combines high strength with lightweight properties, widely used in mechanical and automotive manufacturing.
- 7075: Ultra-high strength, commonly used in aerospace and other demanding applications.
Advantages of Aluminum Flange Materials
- Cost-Effectiveness: Compared to steel flanges, aluminum flanges have lower material and production costs.
- Recyclability: Aluminum is highly recyclable, contributing to sustainable engineering practices.
- High/Low Temperature Resistance: Certain grades (such as 5083) maintain stable performance in a temperature range of -196°C to 150°C.
- Versatility: Available in various sizes and configurations to meet customized design requirements.
- Easy Installation: Lightweight, simplifying operations and reducing transportation costs.
Limitations
- Lower Strength: Weaker in pressure and tensile capacity compared to steel flanges, softens at high temperatures.
- Prone to Deformation: Requires careful bolt torque application during installation to avoid over-tightening.
Applications of Aluminum Flanges
- Industrial Piping Systems: Used for connecting pipes and fittings in manufacturing, chemical processing, and water treatment.
- Marine and Offshore Facilities: Essential where corrosion resistance and weight reduction are critical.
- Water Treatment and Chemical Industries: Used to connect various pipes and equipment for liquid and gas handling.
- Refrigeration and Air Conditioning Systems: Applied in connecting compressors, condensers, and evaporators due to easy handling and efficient heat transfer.
- Industrial Production Lines: Used in automated production lines to connect pipes for material transport or other operations.
- Automotive Manufacturing: Found in engine cooling systems, turbocharger systems, and more.
- Construction Engineering: Used in large-scale piping connections for water supply, drainage, and fire protection systems.
- Aerospace: Used in fuel lines and hydraulic systems due to weight reduction requirements.
Aluminum Flange Standards
Standard Compliance:
Aluminum flanges are typically designed according to standards such as ASME B16.5 and DIN, ensuring consistency and reliability across applications.
International Standards:
- American Standard: ASME B16.5 (Pressure ratings 150#~2500#).
- European Standard: EN 1092-1 (PN6~PN40).
- Japanese Standard: JIS B2220.
Manufacturing Process
Aluminum Flange Manufacturing Methods
Aluminum flanges can be produced through casting, forging, or machining rolled plates. Some special types, such as lap joint flanges, use advanced casting techniques to achieve desired mechanical properties and corrosion resistance.
- Casting Method: Suitable for mass production, cost-effective but may have porosity defects.
- Forging Method: Formed under high pressure, results in dense structure and high strength, ideal for high-pressure environments.
- Machining: Directly cut from aluminum plates or bars, offering high precision and suitable for customized applications.
Forged Aluminum Flanges
Characteristics of Forged Aluminum Flanges
Aluminum alloy flange forging is achieved through hot or cold forging processes, improving material density and mechanical performance to ensure the flange's load-bearing capacity.
- Hot Forging: Performed at high temperatures (typically 300-500°C), enhances material plasticity, facilitates complex shapes, reduces work hardening, and is suitable for large or highly deformed components.
- Cold Forging: Conducted at room temperature, requires higher pressure but improves surface finish and dimensional accuracy, while increasing strength through work hardening (tensile strength can be enhanced by 20%-30%).
Both processes enhance material density, eliminate porosity and shrinkage defects, refine grain structure, and optimize mechanical properties (such as fatigue resistance and toughness), ensuring the flange's high load-bearing capability.
Characteristics of Aluminum Alloy Flange Forgings
- High Strength and Lightweight: The specific strength (strength/density) is close to that of steel, making it suitable for high-pressure pipeline systems.
- Fatigue Resistance: Long service life under cyclic loads, ideal for vibrating environments (such as automotive chassis).
- Application Fields: Aerospace (engine components), automotive (new energy battery trays), petrochemical (corrosion-resistant pipeline connections).
- Economic Efficiency: Although material costs are higher, weight reduction lowers transportation and installation costs, providing significant overall benefits.
Grades and Materials of Aluminum Alloy Flange Forgings
| Grade (ASTM) | Corresponding GB/T Grade | Main Components | Characteristics and Applications |
| 6061 | LD30 | Mg-Si (Primary) | Excellent corrosion resistance, good weldability, medium to high strength, used in general machinery and ships. |
| 7075 | LC9 | Zn-Mg-Cu (High Strength) | Ultra-high strength, used in aircraft landing gear and military components, but requires protection due to lower corrosion resistance. |
| 2024 | LY12 | Cu-Mg (High Toughness) | High fatigue strength, used in aerospace structures (wing skins), requires coating for corrosion protection. |
| 5083 | LF4 | Mg-Mn (Seawater Resistant) | Excellent seawater corrosion resistance, used in ships and offshore platform flanges. |
Aluminum alloy flange forgings optimize performance through the forging process, combining advantages such as lightweight, high strength, and corrosion resistance, and are widely used in high-end industrial fields. Material selection should be based on working conditions (strength, corrosion environment), and appropriate heat treatment should be applied to achieve optimal performance.
Comparison of Aluminum Flanges with Other Material Flanges
| Characteristics | Aluminum Flange | Stainless Steel Flange | Carbon Steel Flange |
| Weight | Lightest | Medium | Heavier |
| Corrosion Resistance | Excellent (except in strong acid/alkali environments) | Superior | Requires coating for corrosion protection |
| Cost | Medium | High | Low |
| Suitable Temperature Range | Moderate | Widest range | Relatively small |
How to Choose the Right Aluminum Flange
Key Parameters for Selecting Aluminum Flanges
- Working Pressure (PN/Class)
- Medium Temperature (typically ≤200°C)
- Pipeline Size (DN/NPS)
- Sealing Surface Type (RF/FF, etc.)
- Compatibility (avoid direct contact with dissimilar metals like copper and steel)
Installation and Maintenance
Installation Tips:
- Clean the sealing surface and use non-metallic gaskets (such as rubber, PTFE) to prevent galvanic corrosion.
- Tighten bolts evenly in a diagonal sequence to prevent flange deformation.
- Avoid direct contact with steel flanges (use insulating gaskets to prevent electrolytic corrosion).
Maintenance Recommendations:
- Regularly check bolt preload and sealing surface condition.
- Apply anodizing treatment in acidic or alkaline environments for enhanced surface protection.
- Ensure pressure and temperature ratings match when replacing flanges.
Aluminum flanges offer unique advantages in lightweight and corrosion resistance, making them irreplaceable in specific industrial scenarios. Selection should consider medium properties, environmental conditions, and cost. Surface treatments (such as hard anodizing) may be applied to enhance wear resistance and strength. For ultra-high-pressure or high-temperature conditions, steel flanges or composite material flanges are recommended.
Aluminum flanges combine lightweight properties, strong mechanical performance, and excellent corrosion resistance, making them an indispensable part of many modern pipeline systems. Whether used as slip-on, weld-neck, threaded, or other configurations, their adaptability and efficiency help ensure reliable, leak-free connections in low- and medium-pressure applications.

